15 Product Planning and Development Process
Product planning and development is a systematic process by which entrepreneurs transform ideas into marketable products or services. It ensures that innovations are not only creative but also feasible, profitable, and aligned with customer needs.
Hisrich, Peters & Shepherd (2020) highlight that product development reduces risk by moving ideas through screening, testing, and validation stages, while Desai (2014) stresses that structured planning increases the chances of long-term success.
15.1 Importance of Product Planning
- Ensures new products meet customer expectations.
- Aligns innovation with market demand and competitive positioning.
- Reduces risk of failure through staged evaluation.
- Provides roadmap for R&D, marketing, and operations.
- Helps attract investors by demonstrating a structured pathway.
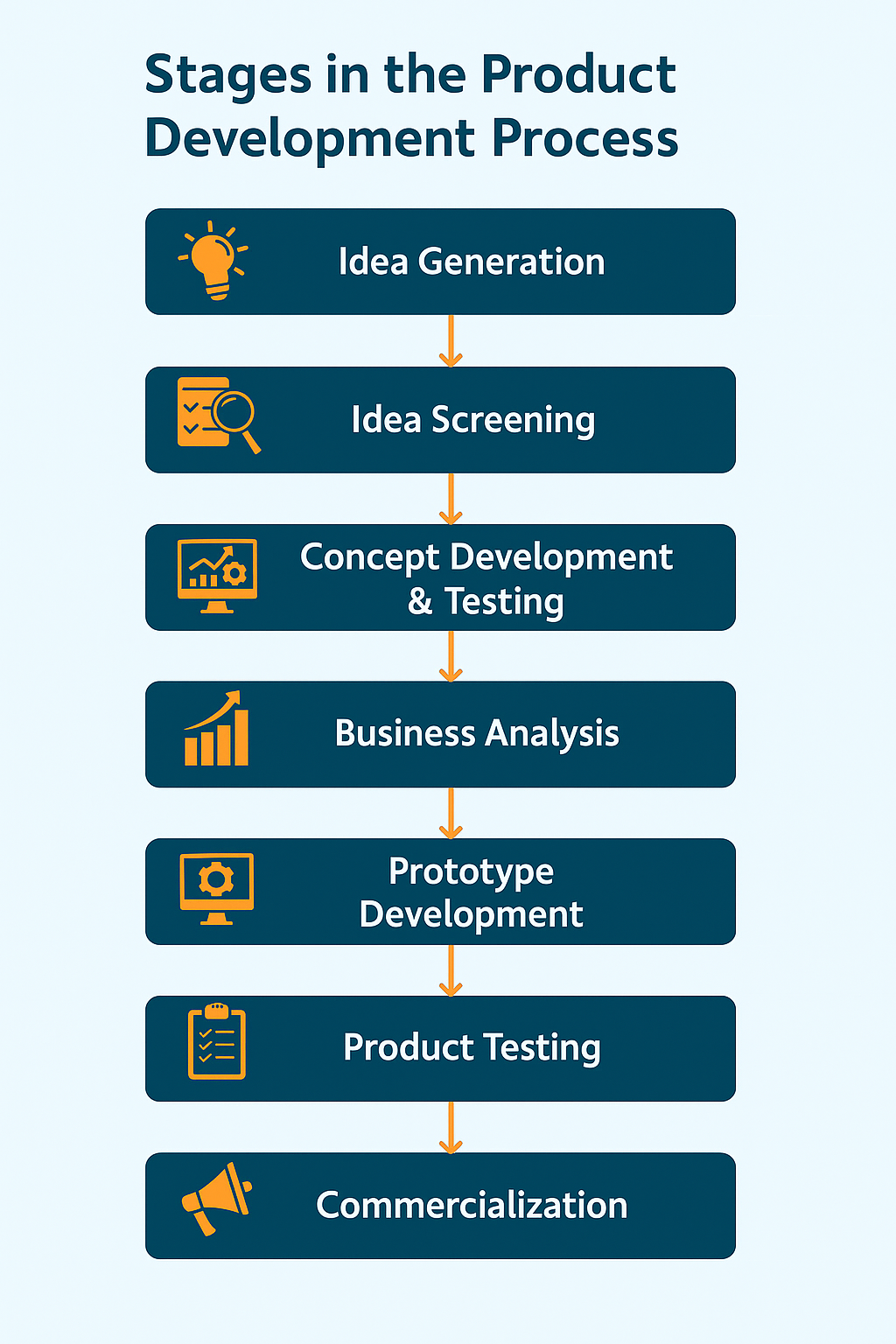
15.2 Stages in the Product Development Process
| Stage | Key Activities | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Idea Generation | Collecting ideas from consumers, markets, and R&D | Ola identifying gaps in urban transport |
| Idea Screening | Filtering out weak or unfeasible ideas | Flipkart starting with books to test demand |
| Concept Development & Testing | Defining features and testing with target users | Zomato testing food delivery features |
| Business Analysis | Estimating costs, revenues, and break-even | Paytm projecting UPI adoption |
| Prototype Development | Creating an initial model (MVP) | BYJU’S developing demo courses |
| Product Testing | Market trials, feedback, refining design | OYO piloting rooms before expansion |
| Commercialization | Full-scale launch with marketing and distribution | Tesla launching EVs globally |
15.3 Models of Product Development
Traditional Stage-Gate Model
Products move through gates where each stage must be approved before proceeding. Ensures control and risk management.
Agile and Lean Development
Focuses on iteration, flexibility, and customer feedback. Popular in software startups.
- Example: SaaS companies like Zoho refine features continuously.
Design Thinking in Development
Human-centered approach combining empathy, ideation, prototyping, and testing.
- Example: Apple using design thinking for iPhone usability.
15.4 Advantages and Limitations
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Product Development | - Reduces risk of failure - Ensures customer orientation - Facilitates investor confidence - Improves efficiency |
- Time-consuming - May stifle creativity if too rigid - Requires significant resources - Rapid market shifts may outpace process |
15.5 Indian Perspective
- Frugal Innovation: Entrepreneurs create affordable, scalable products for mass markets (MittiCool clay fridge, Jaipur Foot).
- IT and EdTech Leadership: Infosys, BYJU’S, and Unacademy show iterative development cycles.
- Policy Support: Make in India and MSME incentives promote manufacturing and product scaling.
15.6 Global Perspective
- USA: Agile and lean models dominate startups (Airbnb, Uber).
- Europe: Strong emphasis on sustainability-focused product development.
- China: Rapid commercialization cycles in e-commerce and electronics (Xiaomi, Huawei).
15.7 Case Studies
- Flipkart (India): Started with books to validate e-commerce before expanding.
- BYJU’S (India): Launched pilot courses before scaling internationally.
- Tesla (USA): Progressed from Roadster prototype to mass-market Model 3.
- Apple (USA): Iterative product development with design-driven innovation.
- M-Pesa (Kenya): Piloted mobile payments before national rollout.
15.8 Product Development Diagram
15.9 Future Outlook
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Enhancing product design and consumer insights.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing accelerating prototype creation.
- Sustainable Products: Eco-friendly designs becoming mainstream.
- Customer Co-Creation: Crowdsourced and community-driven product development.
- Global-Local Hybrids: Products adapted for both global markets and local needs.
15.10 Summary
Product planning and development transforms raw ideas into viable products.
- It follows structured stages: idea generation, screening, concept testing, prototype, and commercialization.
- Models like Stage-Gate, Agile, and Design Thinking ensure customer focus and adaptability.
- Indian examples emphasize frugality and scale, while global ventures highlight sustainability and innovation ecosystems.
In essence, product development provides the bridge between creativity and market success, ensuring that entrepreneurial ideas create long-lasting impact.